- Acronym Guide
- AAM
- ABS
- AC
- ACAS
- ADS-B
- AFAC
- AGL
- AI
- AIM
- ALS
- AM
- AMA
- ANSP
- APPI
- AUV
- AUVSI
- ARPAS-UK
- ASTM
- ATC
- BVLOS
- CAA
- CAAC
- CAB
- CASA
- CATT
- CBO
- CBR
- CBRN
- CDMA
- CDR
- CFR
- COA
- COMINT
- CORS
- COTP
- COTR
- CPTED
- CV
- C2
- DAA
- DEM
- DFI
- DFS
- DGCA
- DHS
- DOD
- DPA
- DPEs
- DRO
- DSM
- DSMX
- DSP
- DSSS
- DTM
- EASA
- EFT
- EO
- EOD
- EO/IR
- ELINT
- EMI
- ESC
- EVLOS
- eVTOLs
- FAA
- FCC
- FCS
- FHSS
- FICCI
- FLIR
- FOB
- FOV
- FPS
- FPV
- GBDAA
- GCP
- GCS
- GDPR
- GNSS
- GPS
- GSD
- GVC
- HDR
- HOGE
- IACRA
- ICAO
- ICS
- IMU
- INS
- IR
- ISA
- ISR
- ITU
- JARUS
- LAAMS
- LAANC
- LAATM
- LAI
- LBA
- LIDAR
- LOS
- LSALT
- MAC
- MAVLink
- MLIT
- MMS
- MSL
- MTOM
- NDAA
- NCSL
- NFZ
- NIST
- NMEA
- NOTAM
- NPA
- NPRM
- NTIA
- OEM
- OFDM
- OOP
- PASM
- PAV
- PCV
- PdM
- PEC
- PIC
- PID
- PIPL
- PLD
- PM
- PN
- PPK
- PPS
- PSM
- PWM
- UAM
- UAOP
- UAS
- UASTM
- UAV
- UCAVs
- UHD
- UHF
- USV
- UTM
- RAIM
- RCC
- RCS
- RFI
- ReOC
- RePL
- RMS
- ROI
- RPAS
- RPC
- RTH
- RTK
- SaR
- SAR
- SARP
- SBAS
- S.Bus
- SBIR
- SEDENA
- SfM
- SFOC
- SIGINT
- SLAM
- SMS
- SORA
- STTR
- sUAS
- TCAS
- TCCA
- TFR
- TIN
- TOF
- TP
- TPS
- TSA
- VHF
- VLOS
- VTOL
Drone Acronyms
What is RFI (Radio Frequency Interference)?
By
Jacob StonerTable Of Contents
Definition
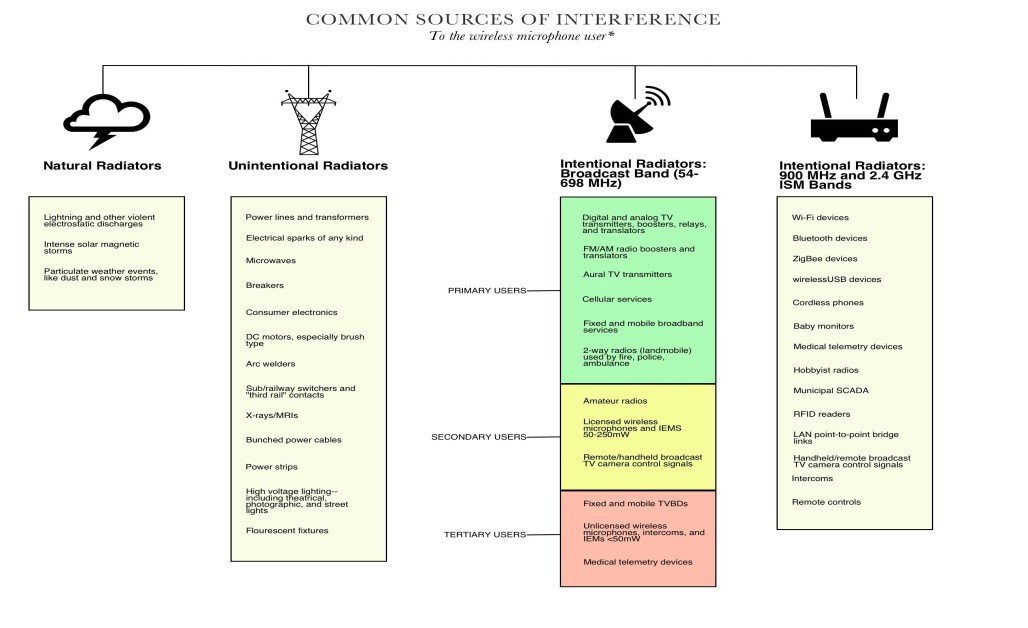
RFI stands for Radio Frequency Interference, which refers to the disruption or degradation of radio signals caused by the presence of unwanted or competing signals in the same frequency range. This interference can come from a variety of sources, such as other electronic devices, power lines, weather conditions, or even other communication systems. RFI can affect a wide range of communication systems, including wireless networks, radio broadcasts, and drone operations.
Usage
RFI is particularly important in drone communication, as interference can disrupt the control signals between the drone and the operator, potentially leading to loss of control or reduced data transmission quality. RFI can affect both telemetry data and video feeds, especially in environments with multiple RF-emitting devices, such as urban areas or industrial zones. Drone operators must be aware of potential sources of RFI and take measures to minimize its impact, such as using frequency-hopping technologies or operating in less congested frequency bands.
Relevance to the Industry
RFI poses a significant challenge in the drone industry because it can lead to unreliable communication, particularly in high-frequency bands where drones typically operate. Understanding and mitigating RFI is crucial for safe drone operations, especially for commercial and industrial applications that rely on uninterrupted data transmission for tasks like mapping, surveillance, or inspection.
How Does Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) Work?
Interference Generation and Signal Disruption:
- Emission of Unwanted Signals:
- Sources of RFI: Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) occurs when unwanted or unintended RF signals are emitted by electronic devices, communication systems, or natural sources, interfering with the proper functioning of other radio frequency-dependent systems. These interfering signals can originate from a variety of sources, including wireless routers, cell towers, power lines, weather conditions, and even other drones operating in the same frequency band. RFI typically affects devices that communicate wirelessly, such as drones, radios, Wi-Fi networks, and GPS systems.
- Frequency Overlap: RFI is most problematic when multiple systems use overlapping frequency bands. For example, if a drone operates on the 2.4 GHz frequency band, interference can occur from other devices that use the same or nearby frequencies, such as Wi-Fi routers, Bluetooth devices, and microwaves. This overlap leads to signal degradation, making it difficult for the receiver (such as a drone or controller) to distinguish between the intended signal and the interfering noise.
- Disruption of Communication and Control:
- Signal Degradation: When RFI is present, it disrupts the communication link between the transmitter and receiver. In drone systems, this means the control signals between the drone and its operator may be weakened or interrupted, causing delayed or lost commands. This can lead to erratic drone behavior, including sudden changes in flight path or, in severe cases, complete loss of control.
- Multipath Interference: RFI can also cause multipath interference, where the signal reflects off surfaces like buildings or the ground, creating multiple paths for the signal to reach the receiver. These multiple signals can interfere with each other, resulting in data errors, noise, or a weaker overall signal. This is particularly problematic in urban environments where drones operate near tall structures.
Effects on Drone Systems:
- Impact on Control and Navigation:
- Loss of Control Signals: In drone systems, control signals are transmitted between the ground control station and the drone via RF links. RFI can distort or block these signals, leading to a loss of control, which can cause the drone to fly unpredictably or fail to respond to commands. In worst-case scenarios, RFI can result in complete signal loss, triggering an automatic return-to-home (RTH) function or causing the drone to land unexpectedly.
- Degraded Telemetry and Video Feeds: RFI can also impact telemetry data transmission, resulting in delayed or inaccurate updates regarding the drone’s position, altitude, speed, and other key metrics. In addition, RFI can cause degradation in live video feeds, creating lag, pixilation, or dropped frames, which can severely affect the operator’s situational awareness, especially during critical operations like inspections, mapping, or surveillance.
- Interference with GPS Signals:
- GPS Signal Jamming: GPS systems, which rely on weak signals transmitted from satellites, are particularly vulnerable to RFI. Even low-level interference from nearby transmitters or electronic devices can reduce the accuracy of GPS positioning or cause a complete signal loss. This poses a significant risk for drones, as GPS signals are crucial for autonomous navigation, waypoint following, and maintaining stable flight.
- Positional Drift and Navigation Errors: When GPS signals are impacted by RFI, the drone’s position can “drift” on the controller’s display, causing the drone to deviate from its intended flight path. In severe cases, drones may lose GPS lock, leading to erratic flight behavior, altitude fluctuations, or the inability to complete pre-planned missions.
Mitigating RFI in Drone Operations:
- Using Spread Spectrum Technologies:
- Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS): FHSS helps reduce RFI by rapidly switching the communication frequency between the drone and the controller. This technique minimizes the time spent on any single frequency, reducing the chance of interference affecting the communication link. By hopping between frequencies, FHSS ensures a more stable and interference-resistant signal.
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS): DSSS spreads the data signal over a wider bandwidth, making it less susceptible to narrowband interference. If a portion of the signal is disrupted by RFI, the system can still recover the original data from the remaining signal, ensuring reliable communication in noisy environments.
- Operating in Less Crowded Frequency Bands:
- Alternative Frequency Bands: Drone operators can avoid heavily used frequencies by switching to less congested bands, such as 5.8 GHz or 900 MHz, where there is less RF traffic. These frequency bands are less likely to experience interference from everyday devices like Wi-Fi routers or cell phones, improving signal clarity and reducing the risk of control loss.
- RF Filtering and Shielding: RF filters can be applied to drones and control systems to block out unwanted frequencies that could interfere with communication. Additionally, shielding techniques can help protect sensitive drone electronics from external RF interference, particularly in industrial or urban environments.
- Signal Monitoring and Pre-Flight Assessments:
- RF Spectrum Analysis: Before flight, operators can use RF spectrum analyzers to scan the operating environment for potential sources of interference. Identifying crowded frequency bands allows operators to adjust their communication setup, such as changing frequency bands or adjusting transmitter power levels, to avoid RFI.
- Interference Detection Systems: Some advanced drones are equipped with interference detection systems that alert the operator to potential RFI issues in real-time. This allows for quick corrective actions, such as switching to a backup communication link or initiating an emergency landing if signal integrity is compromised.
By understanding the sources of RFI, its impact on communication systems, and employing mitigation strategies like spread spectrum technologies and frequency management, drone operators can minimize the risks associated with radio frequency interference and ensure safe and reliable drone operations.
Example in Use
“The drone experienced signal disruption due to radio frequency interference (RFI) from nearby Wi-Fi networks, which caused intermittent control issues during the flight.”
Frequently Asked Questions about RFI (Radio Frequency Interference)
1. What causes RFI?
Answer: RFI can be caused by a variety of sources, including:
- Electronic Devices: Devices like microwaves, computers, and power supplies can emit radio frequency signals that interfere with communication systems.
- Competing Wireless Signals: Other wireless devices, such as Wi-Fi routers, cell phones, and other drones, can create interference, especially when operating on similar frequency bands.
- Environmental Factors: Weather conditions, solar activity, and physical obstructions can also contribute to radio frequency interference.
2. How does RFI affect drone operations?
Answer: RFI can impact drones by:
- Disrupting Control Signals: Interference can weaken or disrupt the signals between the drone and its controller, leading to a loss of control or erratic flight behavior.
- Reducing Data Quality: Video feeds or telemetry data can be degraded, making it difficult for operators to maintain real-time awareness of the drone’s position and performance.
3. How can RFI be mitigated?
Answer: RFI can be mitigated by:
- Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS): This technique allows the communication system to rapidly switch between different frequencies, reducing the likelihood of interference.
- Operating in Less Crowded Bands: Using less congested frequency bands, such as 5.8 GHz or 900 MHz, can help reduce the chances of encountering RFI.
- Shielding and Filtering: Using RF shielding and filters can block unwanted signals from reaching sensitive equipment.
For examples of these acronyms visit our Industries page.
As the CEO of Flyeye.io, Jacob Stoner spearheads the company's operations with his extensive expertise in the drone industry. He is a licensed commercial drone operator in Canada, where he frequently conducts drone inspections. Jacob is a highly respected figure within his local drone community, where he indulges his passion for videography during his leisure time. Above all, Jacob's keen interest lies in the potential societal impact of drone technology advancements.











